Summary
Did you know that X-rays, those images that allow doctors to see through your body, exist thanks to an exceptional female scientist?
Marie Curie, a two-time Nobel Prize winner, revolutionized modern medicine with her discoveries on radioactivity. Yet, in her time, she was repeatedly told that science was not for women. Today, her legacy saves millions of lives and inspires young girls around the world to dare to dream big.
Discover how this outstanding scientist changed medical imaging and why her story should inspire you to become the next genius inventor!
Who was this female scientist who left her mark on the history of science?
Young Marie CURIE
Source : Sciences For Girls AI
A childhood marked by curiosity and determination
Marie Curie, born Maria Skłodowska in 1867 in Warsaw, Poland, showed a keen interest in science and mathematics from a very young age. At a time when women were often excluded from higher education, she attended clandestine classes before going to study at the Sorbonne in Paris. Her journey is a striking example of perseverance: despite the obstacles, she always believed in her dream of becoming a scientist.
A decisive encounter: Pierre Curie
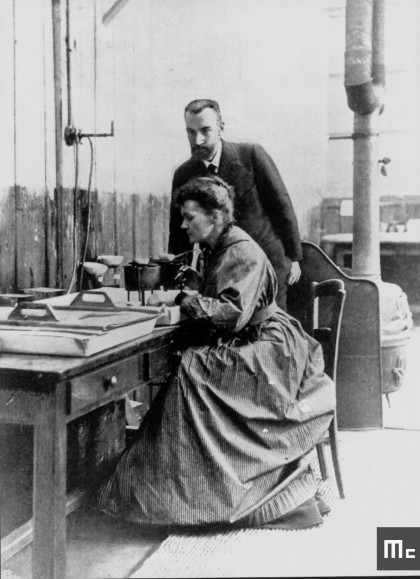
In Paris, Marie Curie met Pierre Curie, a physicist with whom she formed an exceptional scientific partnership. Together, they explored Henri Becquerel’s work on radioactivity. Marie Curie discovered two new elements, polonium and radium, thus laying the foundations of modern medical imaging. Their collaboration demonstrates how teamwork and shared passion can lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
Pierre and Marie CURIE working
Source : https://explore.psl.eu
Two Nobel Prizes, a historic first
In 1903, this scientist became the first woman to receive a Nobel Prize, shared with Pierre Curie and Henri Becquerel, for their work on radioactivity. After Pierre’s tragic death in 1906, she continued her research and won a second Nobel Prize in 1911, this time in chemistry. These awards make her the only person to have been honored in two different scientific fields, undeniable proof of her genius and determination.
Marie Curie and medical imaging: a silent revolution
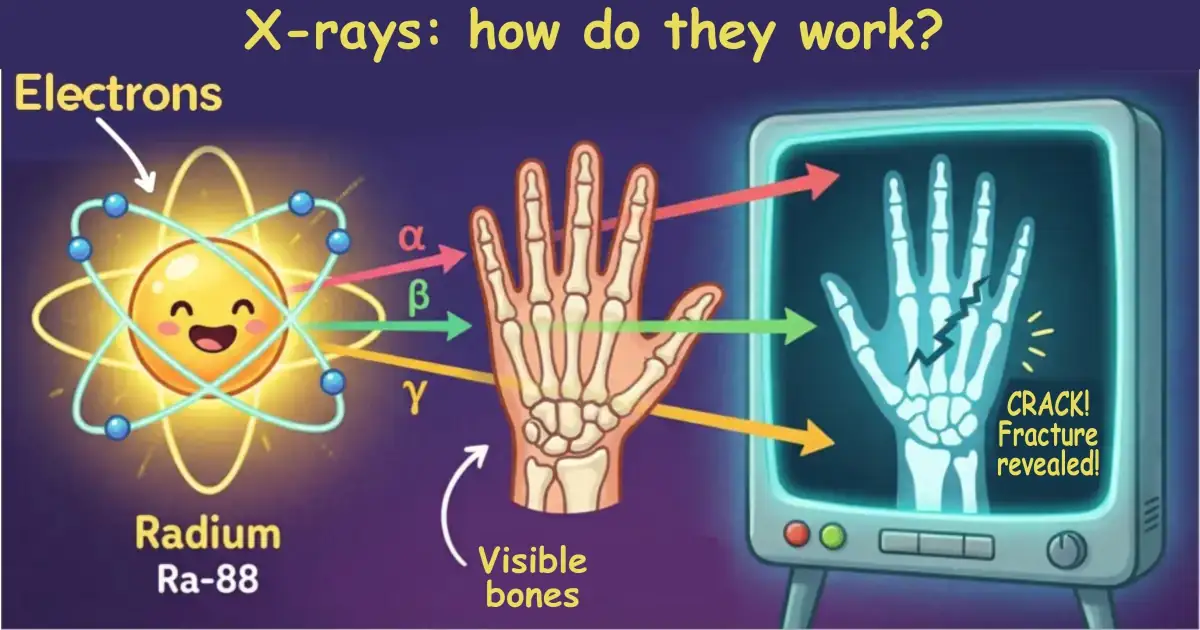
X-rays imaging process
Source : Sciences for Girls
The discovery of radioactivity
Marie Curie understood that certain elements, such as radium, emit rays capable of penetrating matter. This discovery paved the way for radiography, a technique that allows visualization of the inside of the human body without resorting to surgery. Thanks to her work, doctors were able to diagnose fractures, infections, and other pathologies non-invasively, thus transforming medical practice.
The “Little Curies”: radiological ambulances on the front lines
During the First World War, Marie Curie put her knowledge to work for wounded soldiers. She equipped vehicles with portable X-ray machines, nicknamed the “Little Curies.” These mobile units allowed doctors to locate bullets and shrapnel in soldiers’ bodies, saving thousands of lives. Her wartime commitment demonstrates how science can have a concrete and immediate impact on society.
“Little Curie” the radiologic car
Source : Wikimédia
Marie Curie’s legacy in modern medical imaging
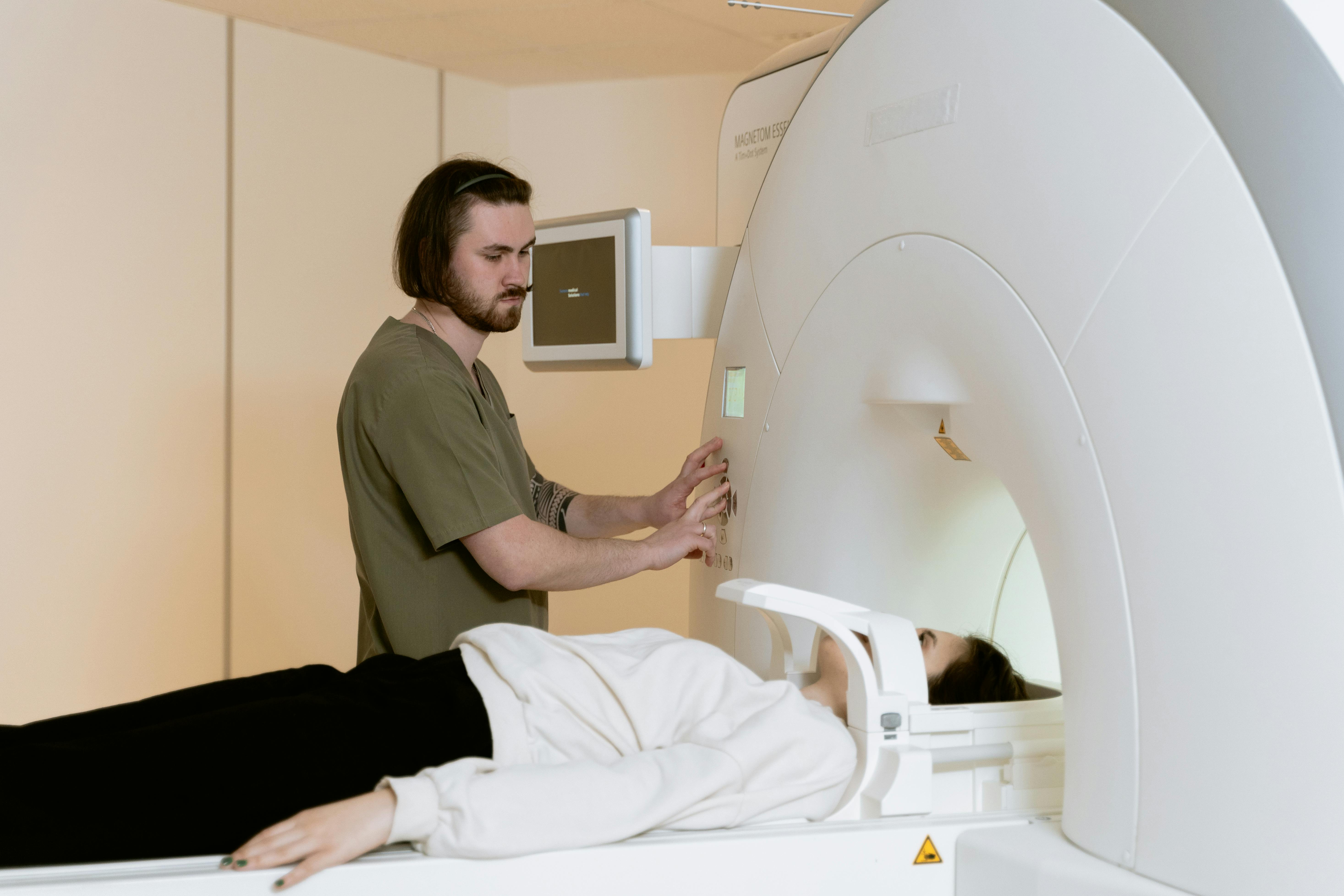
Today, medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and radiotherapy, owe much to the discoveries of Marie Curie. Without her work, these technologies, which save lives every day, might not exist. Her legacy continues to inspire researchers and physicians, reminding us that curiosity and perseverance can lead to major advances for humanity.
Moderne medical imagery
Source : https://images.pexels.com
Why is this scientist a source of inspiration for young girls?
A pioneer in a man’s world
At a time when women were often confined to the traditional roles of mother or wife, Marie Curie proved that a woman could excel in science. She overcame sexism, a lack of resources, and prejudice to become one of the most respected female scientists in history. Her journey demonstrates that barriers can be broken down with courage and determination.
A model of perseverance and passion
Marie Curie worked in difficult conditions, sometimes in a simple, unheated shed, handling radioactive substances without fully understanding their dangers. Despite these challenges, she never abandoned her research. Her story is a powerful reminder that passion and determination can overcome all obstacles, even the most daunting.
A legacy that encourages scientific vocations
Today, many young women still hesitate to pursue careers in science, often fearing they won’t be up to the task or won’t find their place in a predominantly male field. Yet, female scientists like Marie Curie, Rosalind Franklin, and Katherine Johnson have proven that science needs female talent. Their success demonstrates that young women today can become the scientists, engineers, and inventors of tomorrow.
Did you know that, according to UNESCO, only 28% of researchers worldwide are women? And that women represent less than 30% of students in engineering schools? These figures highlight the importance of continuing to encourage young girls to pursue careers in science, in order to close this gap and allow more female talent to flourish.
How to follow in Marie Curie's footsteps?
If you’re a young girl passionate about science and dream of contributing to discoveries like those of Marie Curie, there are many ways to get started. First of all, don’t let anyone tell you that science isn’t for you. Stereotypes have no place in this field, and your potential is limitless.
Finding mentors can also help you progress. Look for female scientists who can guide you, advise you, and share their experience. Their support can be invaluable in directing and motivating you in your studies and projects.
Participating in science workshops or clubs is another excellent way to develop your skills. Many associations and schools offer activities specifically designed for young people, and particularly for girls, to encourage them to explore science in a fun and interactive way.
Reading biographies of female scientists is also an inexhaustible source of inspiration. Discovering the journeys of Marie Curie, Rosalind Franklin, Ada Lovelace, or Mae Jemison, the first African-American woman astronaut, can show you that anything is possible with determination.
Finally, studying science subjects in high school and university is essential to prepare you for a career in this field. Physics, chemistry, biology, and mathematics are disciplines that open many doors to exciting and innovative careers.
A tool to inspire and engage in dialogue with young people: a guide for mentors, parents, and educators
The story of Marie Curie is an inexhaustible source of inspiration for encouraging young girls to take an interest in science. Here are some ideas for using one’s journey as a starting point for enriching discussions and motivating activities.
Start by initiating the conversation with simple, open-ended questions. For example, ask: “What impressed you most about Marie Curie’s story?” or “If you could invent something to help others, like she did with X-rays, what would you choose?”. These questions allow us to address topics such as the perseverance, creativity and the place of women in science.
To make the story more concrete, suggest hands-on activities. A simple experiment with a UV lamp and fluorescent objects can illustrate the principle of radioactivity. You can also take a virtual tour of the Curie Museum in Paris or imagine together a useful invention for medicine, like the “Little Curies”. These activities help young girls to envision themselves in an active and creative role.
Highlight contemporary female role models to show that women continue to make their mark on the history of science. Talk about Emmanuelle Charpentier (2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry), Katie Bouman (who contributed to the first image of a black hole), or Mae Jemison (first African-American woman astronaut). These examples show that the Scientific careers are accessible and exciting for girls today.
Encourage reading and discussion by suggesting books or films about Marie Curie and other women scientists. For example, “Women in Science” by Rachel Ignotofsky or the film “Radioactive”. (2019) are excellent resources for exploring the topic further. After reading or watching, discuss what she learned or what surprised her.
Finally, remind her that setbacks are part of the process scientist. Marie Curie worked in difficult conditions, but she never gave up. Use her example to talk about résilience : “Quels défis es-tu prête à relever pour atteindre tes rêves ?”. By valuing his efforts and ideas, you will help him gain confidence and believe in his potential.
Conclusion: A timeless heroine for women scientists
Marie Curie was not only a brilliant scientist; she was also a courageous woman, a pioneer, and an inspiration to generations of young girls. Her discoveries transformed modern medicine and saved countless lives. Her story reminds us that science has no gender and that every girl has the potential to become the next great inventor or researcher.
So, if you dream of doing science, remember Marie Curie: with passion, work and determination, anything is possible
To go further
- Book : Marie Curie, an honorable woman – Françoise Giroud
- Movie : Radioactive (2019) – A biopic about the life of Marie Curie
- Internet Site : Nobel Prize – Marie Curie